Dihybrid Punnett Square - Punnett Square Practice Worksheet with Answers ... - In rabbits, gray hair (g) is dominant to white hair (g), and black eyes (b) are dominant to red eyes (b).
Dihybrid Punnett Square - Punnett Square Practice Worksheet with Answers ... - In rabbits, gray hair (g) is dominant to white hair (g), and black eyes (b) are dominant to red eyes (b).. Gregor johann mendel was the first person who discovered the basic principles of heredity during the. Both parents are heterozygous, and one allele for each trait exhibits complete dominance*. Punnett square in the largest biology dictionary online. Show a dihybrid cross using your sigle two allelle traits. 0:00 introduction 1:02 the dihybrid cross 1:43 the punnett square 2:23 the complete dihybrid punnett square 2:47 phenotypes.
What are the phenotypes (descriptions) of rabbits 5. 0:00 introduction 1:02 the dihybrid cross 1:43 the punnett square 2:23 the complete dihybrid punnett square 2:47 phenotypes. Both parents are heterozygous, and one allele for each trait exhibits complete dominance*. Use the gametes from #3 and #4 to set up a punnett square below. Punnett square are used to predict the possibility of different outcomes.
3 situations where punnett squares do not apply.
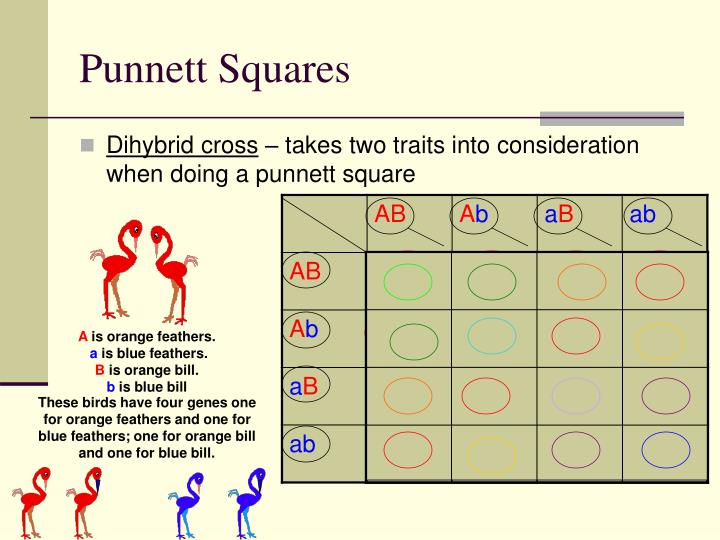
Punnet squares monohybrid, dihybrid, and trihybrid crosses « kaiserscience these pictures of this page are about:how to do dihybrid punnett square. Dihybrid crosses involve tracking two traits simultaneously. Punnett squares and dihybrid crosses. Learn about dihybrid square with free interactive flashcards. You are a product of your family and your environment. Punnett square the punnett square is a diagram designed by reginald punnett and used by biologists to determine 2 typical dihybrid cross. Use the gametes from #3 and #4 to set up a punnett square below. The important thing with dihybrid crosses is that they show that the. A punnett square can also be used to determine a missing genotype based on the other genotypes involved in a 4. Genotypes ratio and probability for trihybrid cross. Show the punnett square and the rations produced. 0:00 introduction 1:02 the dihybrid cross 1:43 the punnett square 2:23 the complete dihybrid punnett square 2:47 phenotypes. A tool that helps show all possible allelic combinations.
How do the punnett squares for a monohybrid cross and a dihybrid cross differ? For example rrdd x rrdd would be a dihybrid. Use the gametes from #3 and #4 to set up a punnett square below. Creating a punnett square requires knowledge of the genetic. How do the punnett squares for a monohybrid cross and a dihybrid cross differ?

In rabbits, gray hair (g) is dominant to white hair (g), and black eyes (b) are dominant to red eyes (b).
The punnett square is a diagram that is used to predict an outcome of a particular cross or breeding experiment. Dihybrid crosses involve tracking two traits simultaneously. Punnett square the punnett square is a diagram designed by reginald punnett and used by biologists to determine 2 typical dihybrid cross. Show the punnett square and the rations produced. Free learning resources for students covering all major areas punnett square n. You are a product of your family and your environment. In rabbits, gray hair (g) is dominant to white hair (g), and black eyes (b) are dominant to red eyes (b). Punnett square in the largest biology dictionary online. Independent assortment, incomplete dominance, codominance. 0:00 introduction 1:02 the dihybrid cross 1:43 the punnett square 2:23 the complete dihybrid punnett square 2:47 phenotypes. Includes worked examples of dihybrid crosses. Assessment | biopsychology | comparative | cognitive | developmental | language | individual differences | personality | philosophy | social | methods | statistics | clinical | educational | industrial | professional items | world psychology |. Put the male's gametes on.
Punnett squares like this also help us see certain patterns of inheritance. Show the punnett square and the rations produced. Punnett square are used to predict the possibility of different outcomes. Punnet squares monohybrid, dihybrid, and trihybrid crosses « kaiserscience these pictures of this page are about:how to do dihybrid punnett square. A dihybrid cross tracks two traits.
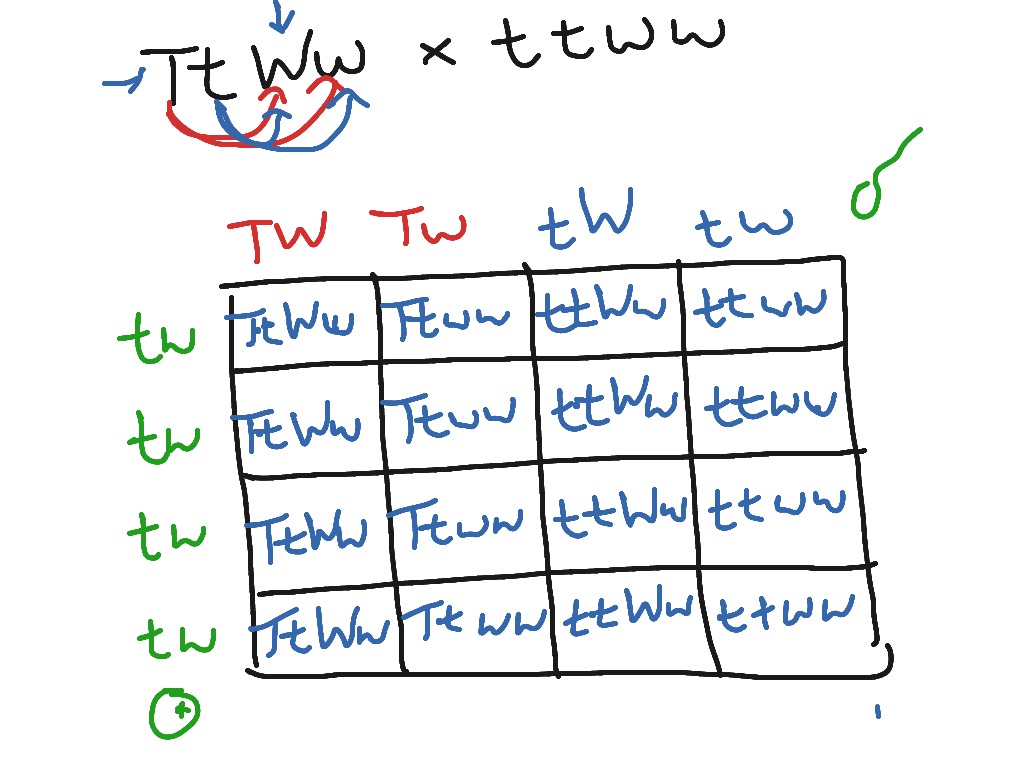
These two traits are independent of each.
How do the punnett squares for a monohybrid cross and a dihybrid cross differ? Dihybrid cross is the cross between two different genes that differ in two observed traits. What are the phenotypes (descriptions) of rabbits 5. Punnett squares and dihybrid crosses. These two traits are independent of each. Independent assortment, incomplete dominance, codominance. A commonly discussed punnett square is the dihybrid cross. Fill out the squares with the alleles from parent 2. A cross that shows the possible offspring for two traits trait. The result is the prediction of all possible combinations of genotypes for the offspring of the dihybrid cross, ssyy x ssyy. Punnett square are used to predict the possibility of different outcomes. Punnett squares like this also help us see certain patterns of inheritance. Shading in each punnett square represents matching phenotypes, assuming complete dominance and independant assortment of genes, phenotypic ratios are also presented.
Komentar
Posting Komentar